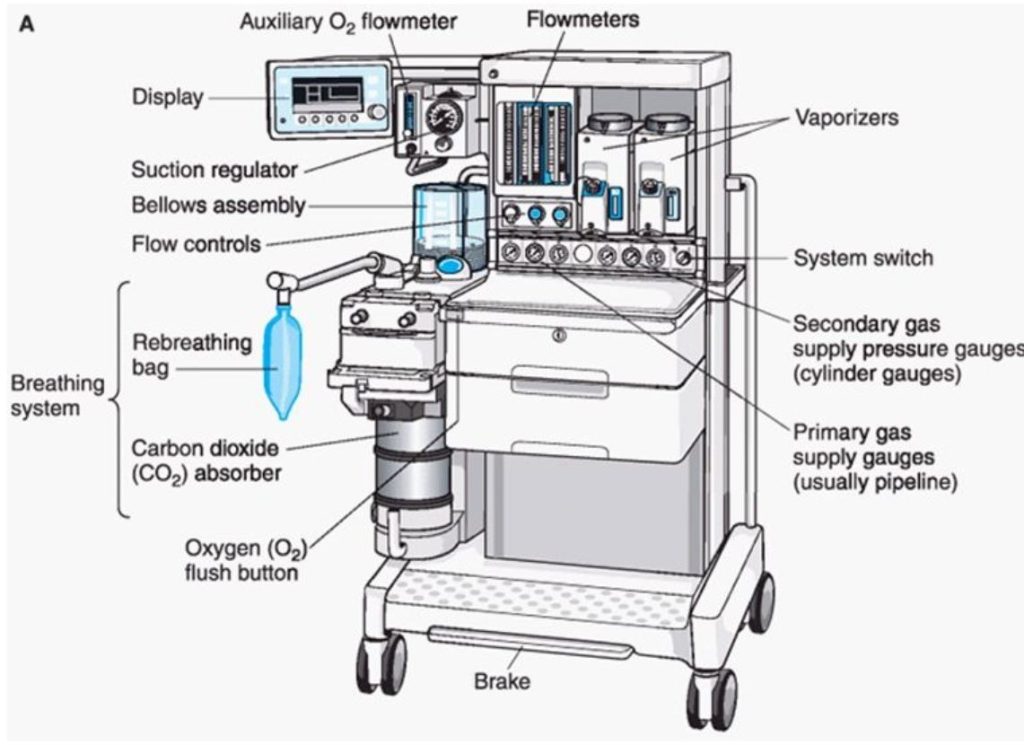
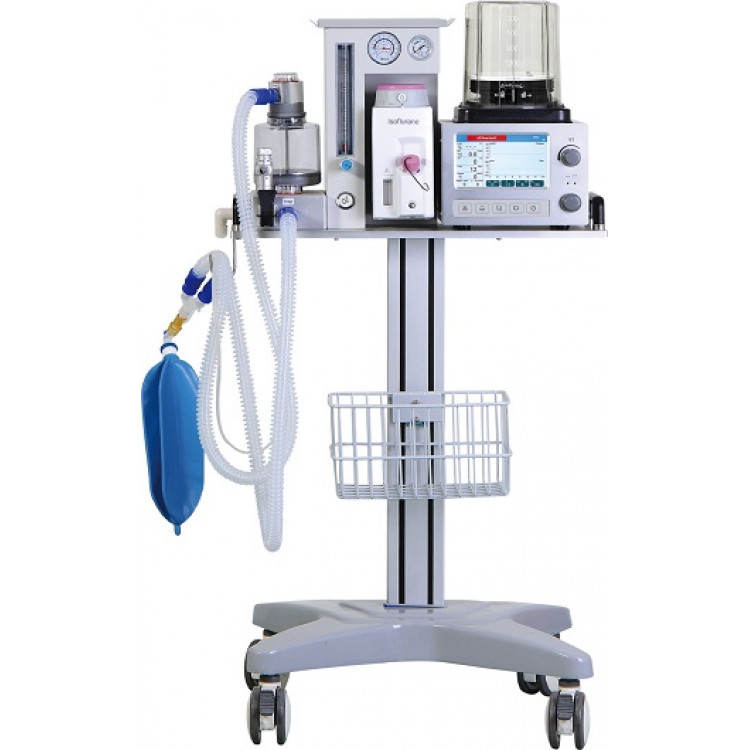
What is anesthesia?
Anesthesia is a medical procedure that makes someone unconscious.
Explanation:
Anesthesia is a medical procedure that makes someone unconscious. This allows them to have surgery, dental work, or other procedures without feeling any pain or discomfort. Anesthesiologists use different types of anesthesia to achieve the desired level of anesthesia for the patient.
Anesthesia can be administered through general anesthetics (such as propofol and etomidate), regional anesthetics (such as lidocaine and bupivacaine), or neuromuscular blocking agents (like atracurium and vecuronium).
The benefits of anesthesia include reduced pain during surgery, decreased anxiety levels in patients, and shorter hospital stays.
What are the different types of anesthesia?
Anesthesia is a medical procedure that stops the sensation of pain. There are four types of anesthesia: general, regional, spinal, and neuromuscular.
Explanation:
General anesthesia is the most common type and works by blocking all sensations from the body. This includes feeling pain, hearing noises, seeing colors, and feeling your body temperature.
Regional anesthesia numbs a specific area of the body only (for example, the arm).
Spinal anesthesia blocks nerve impulses to parts of your spinal cord (thus stopping muscle movement below your waist).
Neuromuscular blockade prevents muscles from contracting (similar to general anesthetics but with more selective effects on certain areas).
Each type has its own benefits and risks associated with it. General anesthetics are generally safe but can cause people to be unable to move or breathe normally if they’re not given correctly. Regional anesthetics may be less safe than general anesthetics but may provide more localized relief for some patients. Spinal anaesthesiologists have greater control over when patients feel pain because they can stop nerve impulses at any time during surgery using spinal anaesthesia techniques such as epidural analgesia or local infiltration with bupivacaine. Neuromuscular blockade is the safest type of anesthesia but may cause more long-term side effects such as paralysis.
How does anesthesia work?
Anesthesia is a type of medical treatment that blocks the sensation of pain.
Explanation:
Anesthesia works by blocking the sensation of pain. This means that people who are under anesthesia don’t feel any pain during or after their surgery.
There are different types of anesthesiologic drugs, and each drug has its own benefits and drawbacks.
The most common type of anesthesiologic drug is general anesthesia (GA), which is used for many types of surgeries. GA also includes regional anesthesia (RA) and local anaesthesia (LA). RA numbs a single area, such as your hand, while LA numbs smaller areas throughout your body.
Anesthesiology is a branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, diagnosis, management and treatmentof diseases by using analgesics
What are the risks of anesthesia?
The risks of anesthesia include: risk of anesthetic overdose, adverse effects from the surgery or drugs, and postoperative complications.
Explanation:
Anesthesia is a procedure that causes you to be unconscious during a medical procedure. The risks of anesthesia include the risk of anesthetic overdose, which can occur if too much medication is given or if there’s something wrong with the equipment used during the operation. Adverse effects from the surgery or drugs may also occur, such as problems breathing after surgery or seizures caused by general anaesthetics. Postoperative complications can range from minor issues like nausea and vomiting to more serious conditions like blood clots in the lungs (pulmonary embolism) or heart attack.
What should you expect after anesthesia?
Every sedation/anesthesia experience is a little different.
Children enter a stage of excitement before drifting off to sleep after anesthesia.
During the “excitement stage,” children are already asleep enough that they do not have control of their movements and don’t remember this phase.
Children may move their arms or legs. Their movements can range from gentle to more forceful, and some appear “seizure-like.”
Some appear dizzy, breathe noisily, or cough.
You may also see unusual eye movements such as eye rolling. This may be upsetting to see, but be assured that this is all very normal during this stage of anesthesia
After anesthesia, you may experience a surreal experience.
You will be given medication to make you comfortable.
Your anesthesiologist will monitor your response to the medication.
Once the medication kicks in, you may feel anxious but will eventually drift off to sleep.




![The [Complete] Guide to Buying Anesthesia Machines](https://www.anesthesia-news.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/anesthesiamachine3.jpg)
![How to Find the [PEEP Valve] on an Anesthesia Machine](https://www.anesthesia-news.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/peep-valve.jpg)